Successful marketing examples from emerging markets teach us many a lesson in getting the basics right.
Let’s take Indonesia for example. While Coke is the beverages leader globally, it is NOT so in Indonesia!
Teh Botol Sosro – The Indonesian Beverages Leader
After 80 years in Indonesia, Coke sells around 80 million cases per annum. Interestingly a local player by name Teh Botol Sosro (TBS) sells 2x that volume. Fascinatingly, TBS is not even a cola, it is a Ready To Drink Tea format and has become Indonesia’s favorite beverage in less than a decade! (source).
The reason? As per this insightful post on Occasion Based Marketing, it is two fold:
(1) TBS’s positioning is grounded in 3 local truths
- Indonesians eat several times each day (3 square meals and 3 to 4 more snacking occasions)
- Indonesia has a strong tea culture
- When Indonesians eat or munch, they feel the need to drink something as well
Given these, TBS positioned itself with the simple and straight forward tagline
“Whatever the meal, Teh botol Sosro is the drink” – (“Apapun makanannya minumnya Teh botol Sosro”).
(2) Discipline in executing marketing strategy
Not only did TBS get the basics right w.r.t the beverages segment, it also ensured robust execution through:
- Consistency of the brand messaging across all touch points
- Ensuring Physical Availability i.e. solid distribution across retail and popular fast food chains like McDonalds and KFC
- Building Mental Availability i.e, driving top of mind awareness and salience by leveraging on all media channels: ATL & BTL
(A Ramadan promo material for TBS, shows the extent of its ‘Physical Availability’ – Image source)
McKinsey & Co Report On Building Brands In Emerging Markets
In many ways, each of the above principles strongly resonate with the findings of a recent McKinsey report titled “Building Brands In Emerging Markets”. Read the full article here for an elaborate report based on research conducted in nine product categories (including food and beverages, consumer electronics, and home and personal-care products) across various developed and emerging markets.
Essentially the report highlights 3 key differences between emerging and developed markets and its implications as:
- Harnessing the power of word of mouth is invaluable, as it seems to play a disproportionate role in the decision journeys of emerging-market consumers.
- Getting brands into a consumer’s initial consideration set is even more important in emerging markets, because that phase of the journey appears to have an out sized impact on purchase decisions.
- Finally, companies need to place special emphasis on what happens when products reach the shelves of retailers, because the in-store phase of the consumer decision journey tends to be longer and more important in emerging markets than in developed ones.
 (Exhibit Source, McKinsey Report On Emerging Markets)
(Exhibit Source, McKinsey Report On Emerging Markets)
While the above example and theory are inspiring and instructive in many ways, these miss out a commentary on an important characteristic of an emerging market.
How about speaking about building CATEGORY RELEVANCE first?
Emerging markets are essentially those where the categories / segments in question are under developed. i.e., the target consumers in these markets don’t find the category/segment relevant to them – at least as yet. So if a segment itself is not seen as relevant in the market place, how crucial are word of mouth / perfect in-store experiences / or consistency in communications for a brand?
As a corollary, brands that start off by ‘setting up the dialogue on a category relevance’ can be said to be leveraging the opportunity to drive awareness of the category/segment and thereby establishing a strong salience of its branded offering in the market. If this key – setting up the context – activity is handled right by a brand, it can naturally have a solid advantage in the market place in the emerging category. Let’s take 2 examples, one from a marketing strategy stand point and the other from a creative execution stand point.
1. Wines in India – Marketing Strategy In An Emerging Market
Wines in India is still an emerging market. In 2012, wine (including imported varieties and sherry) only made up 0.45% of sales of 9 liter cases of alcohol in the country! (source). In other words (for various reasons) wines as an offering in India are still not seen as ‘relevant’ in the consideration set of alcoholic beverages category by most target consumers. So how do you build relevance for wines?
Sula Wines – a pioneer at the forefront of the Indian wine revolution shows by example. It embarked on a set of relevance building initiatives for the segment by going all out to promote wines domestically.For example, it holds about 1,600 wine tasting sessions a year to educate people on the finer points of enjoying a glass of wine, off late it has also been actively developing ‘wine tourism in India’ with vineyard tours and a music festivals held at its winery.
As a result the company produced 550,000 cases of wine last year and expects the number to rise by 25% in 2013. (source)
(Image Source, Kebab Fest @ Sula Wines)
2. 4×4 Drives in Venezuela – Creative Executions In Emerging Markets
Venezuela has 147 motor vehicles per 1000 inhabitants. Compare this with 797 motor vehicles per 1000 that USA has (source). Motor vehicle here is defined as automobiles, SUVs, vans, buses, commercial vehicles and freight motor road vehicles.
So how does Jeep communicate in each of these two markets?
You guessed it right! In a market like Venezuela, Jeep focuses on setting the category context first – i.e. it’s communications are tuned towards building relevance of GETTING OUT as an activity ; and not so much on its technical specifications or competitive claims. See the following print ads by Leo Burnett developed for Venezuela. I love how Jeep manages to drive relevance of its segment without losing its tongue in cheek tone.
 (Source, See the other ads in this series here, agency Leo Burnett)
(Source, See the other ads in this series here, agency Leo Burnett)
On a related note, see how Jeep communicates in Bolivia here. Similar theme here too – More focus on setting up the category relevance than on proclaiming its uniqueness / superiority vs competition.
Now, as a contrast, how does Jeep communicate in the US?
It still speaks in its tongue in cheek tone, it still speaks about getting out or making the world your playground. But here, it also focuses on what makes Jeep the best in its segment by rattling off the pertinent technical specs or superiority credentials. See the following print ad from the US.
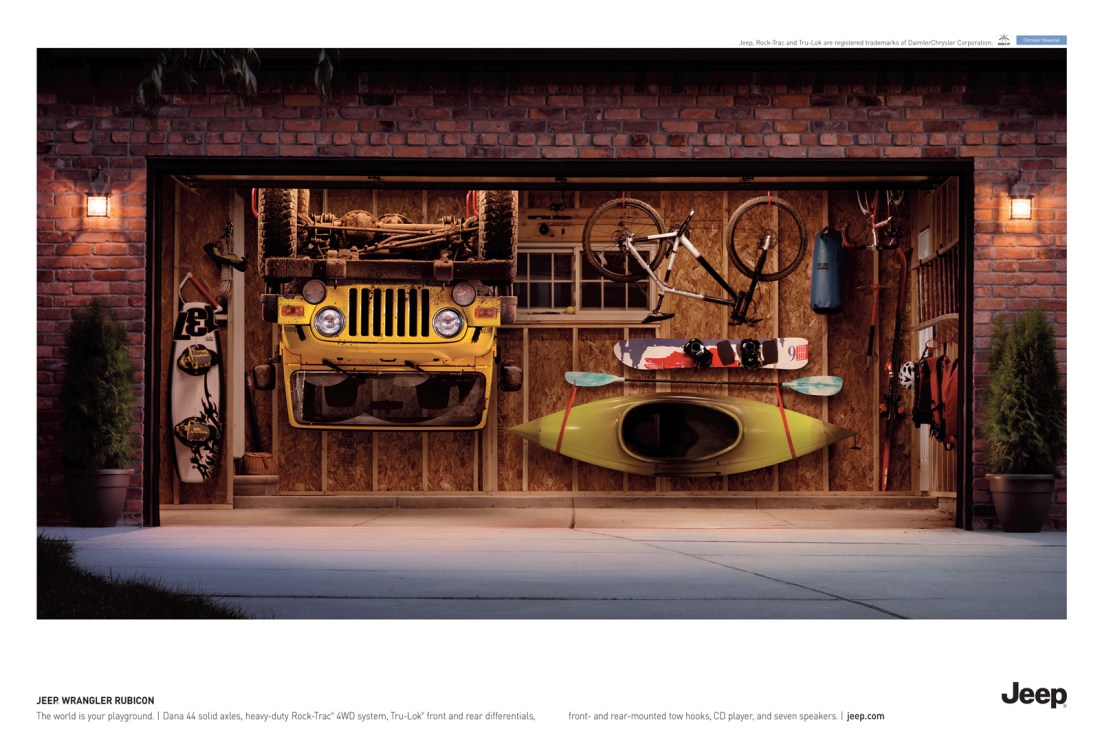 (Source, Click on the ad for the enlarged version, agency BBDO)
(Source, Click on the ad for the enlarged version, agency BBDO)
The copy says: “Dana 44 solid axles, heavu duty Rock-Trac 4WD system, Tru-Lok fornt and rear differentails, front and rear mounted tow hooks, CD player, and seven speakers.”
On a related note, see Jeep’s print ad for Germany (another developed market) here and here. Similar theme here too as that in the US – The focus here is on reinforcing its uniqueness and/or technical superiority vs competition and not so much on setting up the context / category relevance.
In Summary..
Whether it’s about a marketing strategy or even a creative execution, whenever we see a success/failure of a brand in the context of an emerging market, probably the first questions to be asked could as well be:
- Who was the first to drive the category/segment relevance in the market place? (who initiated the dialogue)
- And How? (is the dialogue grounded in local consumer truths?)
Once you have these answers, often times, you might not need to see the market shares for validation.
Don’t you think so?
(Featured Image – BRIC Countries, Source)